

MEASURING GAINS OF TRANSISTORS
Transistor junctions can be measured for go/no go situations, but the test gives no indication of what the current gain maybe.
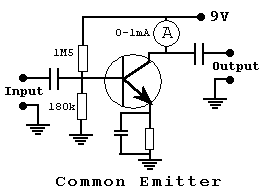
A simple circuit can be constructed as shown with a fixed base current of 5 micro amps the collector current can be measured and so give an indication of current gain.
Try testing a number of transistors and work out their current gain. Results from a batch of transistors may be as follows.
| An approximate gain table | |
| Meter reading | hfe |
| 1mA | 200 |
| 0.9mA | 180 |
| 0.8mA | 160 |
| 0.7mA | 150 |
| 0.6mA | 120 |
| 0.5mA | 100 |
| 0.4mA | 80 |
| 0.3mA | 60 |
| 0.2mA | 40 |
| 0.1mA | 20 |
The results obtained in the table are achieved because the two base resistors maintain a current flow of 5 micro amps.
To carry out the same tests with PNP transistors use the same circuit but just reverse the supply connections. (A PNP transistor has to be biased on from the negative rail).
RULES FOR SUBSTITUTION a transistor in a circuit.
The origin of some of the text on this page is from the RSGB with additions by the web master
To Semiconductor Devices - Transistor Failure