|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
Syllabus Sections:- 6b Ionosphere 5B1 36 Understand the effects of Solar flares and sun spots on propagation Amazingly it has been found that the number of sunspots on the Sun has a considerable effect on propagation. Higher
radio frequencies than say above 30MHz cannot normally be
reflected by the ionosphere and thus pass through to reach
satellites etc. However because of the fact that the greater
the number of sunspots, the greater the levels of radiation
emitted by the sun, which enhances the ionisation of the
ionosphere. This leads to the higher frequencies being
reflected from the ionosphere. Whilst
Solar flares and Coronal
Mass Ejections (CMEs) send enormous amounts of energy and
charged particles towards the earth, where they collide with
the Ionosphere will/may cause geomagnetic storms. These
charged particles cause disturbances in the Earth's magnetic
field, generating significant adverse effects on electrical
systems and communication by radio waves and even telephone
lines. Black outs due to lost of power from power stations and
radio black outs can and do occur.  page 81 onward.
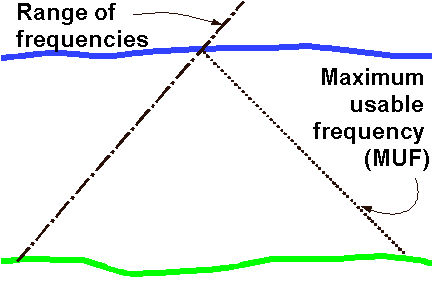
page 81 onward.5B2 36 Recall that the highest frequency that will be refracted back to the transmitter is known as the Critical Frequency of Vertical Incidence (critical frequency). If a range of frequencies from say 1MHz to 144MHz are transmitted vertically towards the ionosphere then in the range of frequencies there will be a frequency which is transmitted but not reflected back to earth. The maximum frequency which is transmitted and returned to earth on a vertical path is called the Critical Frequency of Vertical Incidence or just Critical frequency.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5B2 36 continued Recall the 'Maximum Usable Frequency' (MUF) and that this will be higher than the critical frequency. The Maximum usable frequency (MUF) is just what is says it is. It is the maximum frequency that reliable communication can take place over a know given path. The MUF is in fact a higher frequency than the Critical Frequency due to the fact that the critical frequency is a measure of what can be reflected when it meets the ionosphere at right angles to the layers, where as the MUF is meeting the ionosphere at a lower angle. Thus higher frequencies than the Critical Frequency will continue to pass into outer space until the angle of at which the signal meets the ionosphere is low enough to reflect the signal. Similarly if there is a known path then the frequency can be raised higher than the Critical Frequency until it is not received at which point the MUF has been reached.
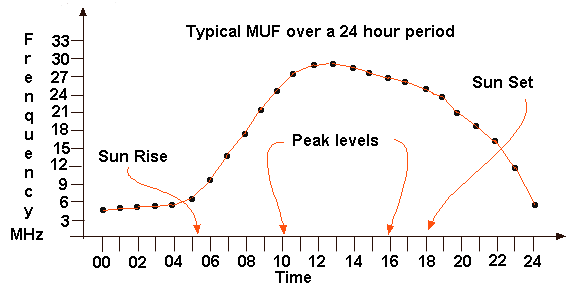
5B2 36 continued Recall, in general terms how the MUF varies over the 24 hour cycle and the variation in MUF from summer to winter. The diagram is a most simplified version of what happens to MUF, which are approximate only, over a 24 hour period without consideration of any special sun activity which can lead to enhanced propagation. The pattern to understand is that the MUF remain low until the sun rises and then there is a relatively steep increase in MUF until midday the highest point of the sun and then the decline in MUF is at a slower rate than the increase until sun set and then the decrease accelerates again until it reaches it lowest level about midnight. The peak levels of MUF are between 10:00 and 16:00 hrs Summer and Winter but in the Summer the MUF will reach higher frequencies than in the Winter as the sun's rays are weaker in winter.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 5B3 36 Recall that propagation where the signals are reflected vertically back from the ionosphere is known as Near Vertical Incidence Sky wave (NVIS) NVIS known as Near Vertical Incidence Sky wave propagation is so called as the radio waves are intended to leave the antenna and propagate vertically to the ionosphere and then are reflected back also vertically forming "a cone of coverage" on the ground of about 10 to 100km. This form of propagation is used on the MF and HF bands to provide radio communications over the relatively short distances and thus can "hop" over mountains or other terrain obstacles. 5B3 36 continued Recall that NVIS is a technique employed on some low frequency bands (e.g. 5MHz) to make contact over relatively short distances. NVIS can be used principally on the lower HF bands for Amateur Radio e.g. 3.5MHz and 5MHz and to a lesser extent on 7MHz with coverage up to about 100kms.5B4 36 continued Recall that the ionosphere can change the polarisation of a radio wave. Due to the very nature of the ionosphere not being a perfect mirror to HF signals the radio wave can be caused to change polarisation in their travel to and from the ionosphere especially where multiple hops occur.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||