

Revision - not in the 2024 Full Syllabus:
Know that the root mean square (RMS) value of a sinusoidal current has the same heating effect as a direct current of the same value and is 0·707 of its peak value.
So where do we find a sinusoidal current. You should understand from earlier FLC and ILC topics that Mains electricity AC has a sinusoidal wave form as the voltage changes from zero to maximum positive and then zero and then maximum negative and then back to zero. You should also then know that if a current is flowing in an AC circuit then as the voltage changes so does the current according to Ohms Law V = I x R
Take a look at the sine wave that you were first introduced to in the Foundation Licence course, but several new items are added in this course.
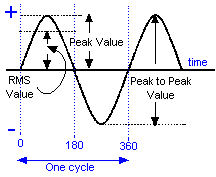
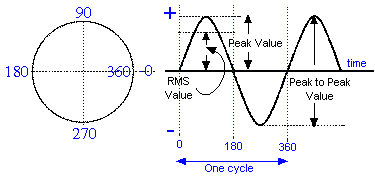
Up to now you have only been considering that part of the sine wave marked 0 to 360 (where it says one cycle in the drawing above) but you have to understand that the sine wave does in fact continues on indefinitely until the source of the sine wave is turned off.
Looking at the diagram you can see Peak Value. This is the maximum voltage of the sine wave. Knowledge of this is needed to understand RMS. RMS stands for ROOT MEAN SQUARE.
If you have a Direct Current from a DC source such as a Battery or Amateur Radio Power Supply and apply it to a circuit with a resistor in it then a current will flow and the resistor will warm up. The heating effect in the resistor will be according to the equation Power in watts = Volts x Current
P = V x I which you learned at FLC level.
Looking at the diagram ABOVE you can see words RMS Value. The RMS value is numerically equal to 0.707 of the Peak value as given by the equation below.
Taking this a bit further the RMS has the same heating effect as a Direct Current of the same numeric value. So if RMS value of the AC wave form is say 220V and the DC is 220V the heating effect will be exactly the same for the AC source and the DC source.
The square root of 2 is 1.414 then 1 divided by square root of 2 equals 0.707. Check that on your calculator even a simple one will give you the result!!
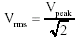

which is
the same as Vrms = Vpeak x 0.707
Thus if the peak value was 240V AC the RMS would be 240 x 0.707 = 169. So if you had a DC voltage you would only need to have a voltage of 169 volts to give the same heating as 240V AC.
In actual fact when we say mains voltage is 230V that is the RMS value - its peak is much higher ! Can you calculate it?
Also observe that the measurement between one peak maximum positive and the peak maximum negative is called the Peak to Peak value.
Finally the horizontal axis through the centre is the time axis and is measured in seconds. The vertical axis is the + and - volts.
Not in the 2024 Full Syllabus
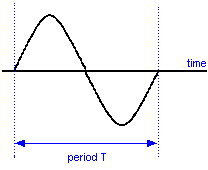
Recall that the period of a sine wave is equal to 1/f and that the frequency of a sine wave is equal to 1/T (where f = frequency in Hertz and T = time in seconds).
There is more about the sine wave that you need to know.
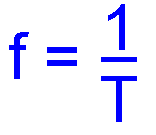
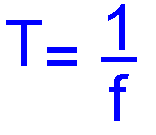

Example
If an RF signal has a frequency of 5MHz what is its periodic time ?
A 2ms B 2u sec C 200n sec D 2 sec
Answer 5MHz is 5,000,000 cycles in one second, so to find the period it is simply one second divided by the number of cycles. (from T = 1/f )
1 / 5000000 = 0.0000002 or 200ns ( nano seconds )
so correct answer is C
Not in the 2024 Full Syllabus
Understand the concept of phase difference, that it is expressed in degrees and that a full cycle is equal to 360 degrees.
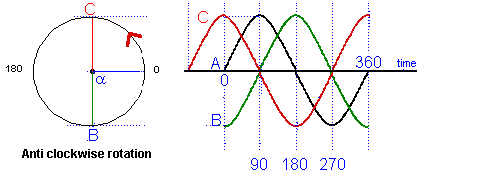
As well as measuring time in seconds it is also referred to as so many degrees. Have a look at the diagram below. Note the progression rotates anticlockwise
You can see that there are markings at the bottom of 0 - 180 - 360 which are measurements in degrees. There are 360 degrees in a circle (see diagram above) just as there are in one cycle of the sine wave.
Phase
The word phase is used in the context of the waveform to mean an amount of time. The amount of time to do one complete cycle is 360 degrees, and half a cycle 180 and so on.
Phase angle
Thus if two sine waves are on the same diagram but start and finish at different places the time difference between them can be
Out of phase
The amount that a curve lags or leads is given in degrees according
to where the same point on the first curve the second one is. In
the diagram above you can see that the angle ![]() = 90o so by using the
circle you could assess the amount of lead or lag in degrees.
= 90o so by using the
circle you could assess the amount of lead or lag in degrees.
From the point of view of the sine wave "A" at point 0, the wave form "C" is leading wave "A" by 90 degrees. If you look at the diagram above "C" as it was at the same point on the time line 90 degree earlier than "A".
Where as wave "B" lags wave "A" by 90 degrees as it has not yet reached the point on the time line where "A" is at 0.
All the waves "A", "B" and "C" are said to be out of phase.
When trying to assess the amount of out of phase, the leading or lagging of one wave form to another you have to assess the location of the peaks that will indicate to you which wave form is ahead or behind and then consider where they respectively cross the ZERO line as here you will be able to use the graticule to count up the number of degree lag or lead.
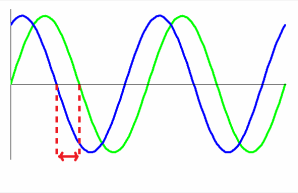
In the diagram above the blue wave form is leading the green wave form and the amount of the lead would be assessed on the zero line where the two dotted red line indicate.
In phase
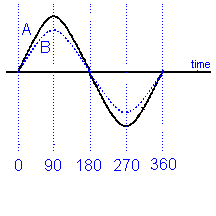
If two curves start and finish at the same time even though they have different magnitudes they are said to be in phase.
All of the above are difficult concepts so make sure you understand them before pressing on.
The origin of some of the text on this page is from the RSGB with additions by the web master