



2D1 Recall that a capacitor consists of two metal plates separated by an insulating material.
The simplest of all capacitors is two pieces of conductive material (metal plates) separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. The dielectric can be as simple as air or it could be plastic, or in fact anything that is an insulator. The dielectric does not need to surround the plates but just to separate them.

Understand that a capacitor can store an electric charge, and that its ability to store a charge (capacitance) depends upon the area of the plates, their separation and the nature of the material between the plates (the dielectric).
Even the two metal plates as a capacitor has the ability to store an electric charge and that the term given to this ability to store the charge is called capacitance.
The size of the capacitance is depended upon the area of the plates and the amount of their separation. The bigger the plates the greater the charge that can be stored and the closer together the plates are also the bigger the charge.


The electric charge can be provided to the plates by attaching a positive link to a battery to one plate and a negative link to a battery to the other plate. A current will flow but only until the potential difference on the places equates to that of the battery. Then the current stops flowing.
The dielectric, that is between the plates will also have an effect on the charge that can be stored.
2D2 Understand and apply the formulae for calculating the combined values of two or three capacitors in series and in parallel.
Formulae for Capacitors
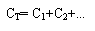
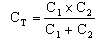
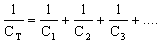
Series Connected Capacitors
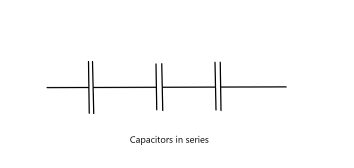
When capacitors are linked in series the total value can be calculated from the formula:-
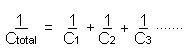
The special case is when there are two capacitors linked in series, then the simplified formula can be used :-
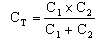
Parallel Connected Capacitors
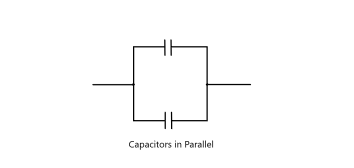
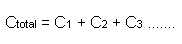

2D3 Recall that some capacitors eg
electrolytic are polarised and must be correctly connected
to avoid injury, damage or destruction.
There are two main categories of capacitor polarised and non polarised and then subdivisions of these categories into various type according to their construction.
With the non polarised capacitor it may be connected into a circuit and the capacitor does not mind which way round its terminals are connected.
 Students are not
picking up this important point that if a polarised capacitor is connected
into a circuit and care is not taken to ensure that the positive side is
connected the positive feed and the negative to the negative feed or there
is a risk of an explosion of the capacitor.
Students are not
picking up this important point that if a polarised capacitor is connected
into a circuit and care is not taken to ensure that the positive side is
connected the positive feed and the negative to the negative feed or there
is a risk of an explosion of the capacitor.
 Large Capacitors
that are polarised must be connected in the circuit with the correct polarity
by reference to the circuit.
Large Capacitors
that are polarised must be connected in the circuit with the correct polarity
by reference to the circuit.
The larger value capacitors are of the polarised style and thus due to their bigger capacity pose and even greater danger if incorrectly connected into a circuit !
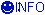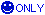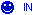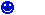
It is necessary to know that capacitors have 3 different circuit diagram symbols.
|
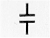 |
Standard (general) capacitor where does not matter which way round it is connected. |
|
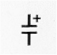 |
Polarised capacitor where it does matter which way round it is connected. |
|
 |
Variable capacitor. |